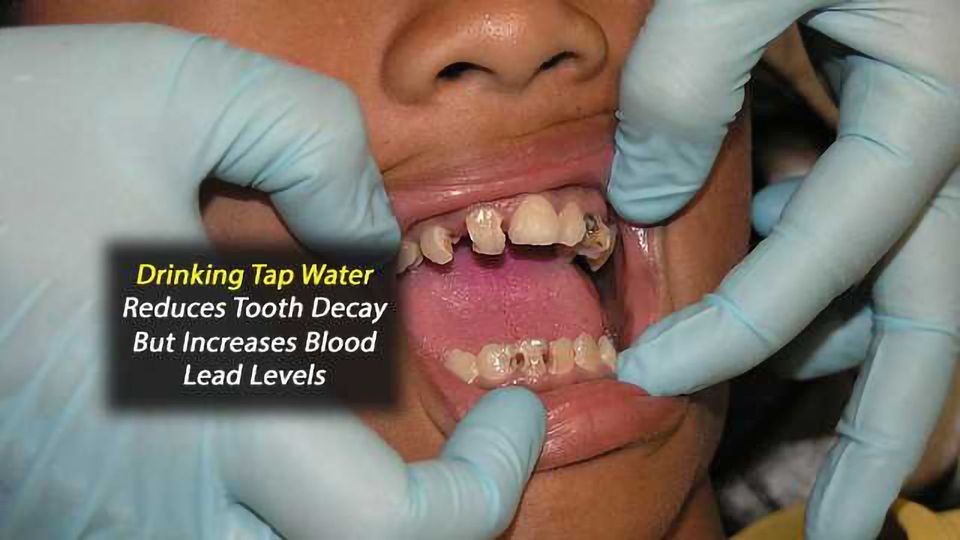
Blood Lead Levels Lower, But Tooth Decay Higher in Children Who Do Not Drink Tap Water
Complete the form below to unlock access to ALL audio articles.
American children and adolescents who do not drink tap water, which is typically fluoridated, are much more likely to have tooth decay, according to a new study in the American Journal of Preventive Medicine. However, the study confirms that those who drink tap water are more likely to have elevated levels of lead in their blood.
Public awareness of the hazards of lead-contaminated water has increased since 2014, when concerns were raised after the drinking water source for Flint, Michigan was changed to the untreated Flint River. A federal state of emergency was declared and Flint residents were instructed to use only bottled or filtered water for drinking, cooking, cleaning, and bathing.
Even before the Flint water crisis, there was public mistrust of tap water safety. But avoiding fluoridated tap water raises another public health concern; children are denied its protection from tooth decay. According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), adding fluoride to the water supply has dramatically reduced the prevalence of tooth decay over the past 70 years. However, tooth decay remains widespread. In 2011–2012, it affected the primary teeth of 23% of U.S. preschoolers.
Anne E. Sanders, PhD, and Gary D. Slade, BDSc, PhD, of the Department of Dental Ecology, University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill, analyzed a nationally representative sample of nearly 16,000 children and adolescents aged two to 19 years who participated in the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES) from 2005 to 2014. More than 12,000 records included data on blood lead level and about 5,600 had dental caries examination data. NHANES is the U.S. benchmark for national surveillance of blood lead levels and is the sole national source of dental examination data.
Following an in-home interview, participants visited a mobile examination center where they donated a blood sample, completed a dietary interview, and received a dental examination. About 15% of the children stated that they did not drink tap water. An elevated blood lead level was defined as having at least three micrograms of lead per deciliter of blood. Tooth decay was defined as the presence of one of more tooth surfaces affected by dental caries as determined by dental examiners using a standardized protocol.
According to the results of this study, children and adolescents who did not drink tap water were more likely than tap water drinkers to have tooth decay, but were less likely to have elevated blood lead levels. Those who drank tap water had significantly higher prevalence of elevated blood lead levels than children who did not drink tap water. Overall, nearly 3% of children and adolescents had elevated blood lead levels and 49.8% had tooth decay. Among American children and adolescents, one in five living below the federal poverty level, one in four African Americans, and one in three Mexican Americans do not drink tap water, vastly exceeding the one in twelve non-Hispanic white children who do not.
“Elevated blood lead levels affect only a small minority of children, but the health consequences are profound and permanent,” explained Sanders. “On the other hand, tooth decay affects one in every two children, and its consequences, such as toothache, are immediate and costly to treat.”
The statistical analysis took into account other factors that could account for the relationship between non-consumption of tap water and blood lead levels and tooth decay. A limitation of the study was that the fluoridation status of participants’ tap water was unknown, so the observation that drinking tap water protects against tooth decay may be an underestimate of fluoride’s protective effect.
“Our study draws attention to a critical trade-off for parents: children who drink tap water are more likely to have elevated blood lead levels, yet children who avoid tap water are more likely to have tooth decay,” commented Slade. “Community water fluoridation benefits all people, irrespective of their income or ability to obtain routine dental care. Yet we jeopardize this public good when people have any reason to believe their drinking water is unsafe.”
This article has been republished from materials provided by Elsevier. Note: material may have been edited for length and content. For further information, please contact the cited source.
Reference
Anne E. Sanders, Gary D. Slade. Blood Lead Levels and Dental Caries in U.S. Children Who Do Not Drink Tap Water. American Journal of Preventive Medicine, 2017; DOI: 10.1016/j.amepre.2017.09.004.